- 您现在的位置:买卖IC网 > Sheet目录2001 > ISL12057IUZ (Intersil)IC RTC/CALENDAR I2C 8-MSOP
13
FN6755.1
March 3, 2011
Device Addressing
Following a start condition, the master must output a Slave
Address Byte. The seven MSBs are the device identifier.
These bits are “1101000”. Slave bits “1101” access the
register. Slave bits “000” specify the device select bits.
The last bit of the Slave Address Byte defines a read or write
operation to be performed. When this R/W bit is a “1”, then a
read operation is selected. A “0” selects a write operation
(see Figure 10).
After loading the entire Slave Address Byte from the SDA
bus, the ISL12057 compares the device identifier and device
select bits with “1101000”. Upon a correct compare, the
device outputs an acknowledge on the SDA line.
Following the Slave Byte is a one-byte word address. The
word address is either supplied by the master device or
obtained from an internal counter. On power-up, the internal
address counter is set to address 0h, so a current address
read of the RTC array starts at address 0h. When required,
as part of a random read, the master must supply the 1 Word
Address Bytes as shown in Figure 11.
In a random read operation, the slave byte in the “dummy
write” portion must match the slave byte in the “read”
section. For a random read of the Clock/Control Registers,
the slave byte must be “1101000x” in both places.
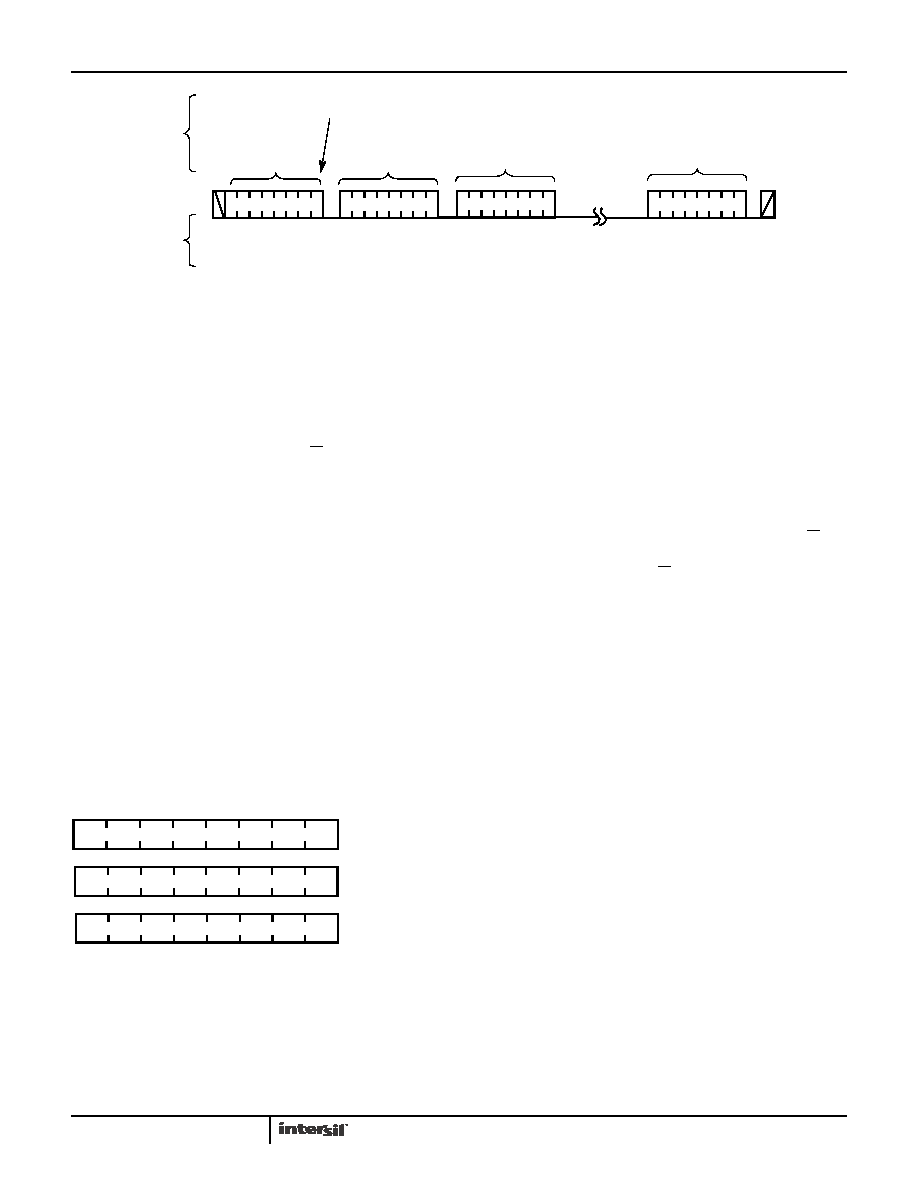
Write Operation
A Write operation requires a START condition, followed by a
valid Identification Byte, a valid Address Byte, a Data Byte,
and a STOP condition. After each of the three bytes, the
ISL12057 responds with an ACK. At this point, the I2C
interface enters a standby state.
Read Operation
A Read operation consists of a 3- byte instruction followed
by one or more Data Bytes (see Figure 11). The master
device initiates the operation by issuing the following
sequence: a START, the Identification byte with the R/W bit
set to “0”, an Address Byte, a second START, and a second
Identification byte with the R/W bit set to “1”. After each of
the three bytes, the ISL12057 responds with an ACK. Then,
the ISL12057 transmits Data Bytes, as long as the master
device responds with an ACK during the SCL cycle following
the eighth bit of each byte. The master device terminates the
read operation (issuing a STOP condition) following the last
bit of the last Data Byte (see Figure 11).
The Data Bytes are from the memory location indicated by
an internal pointer. This pointer’s initial value is determined
by the Address Byte in the Read operation instruction. It
increments by one during transmission of each Data Byte.
After reaching the memory location 13h, the pointer “rolls
over” to 00h, and the device continues to output data for
each ACK received.
FIGURE 9. SEQUENTIAL BYTE WRITE SEQUENCE
S
T
A
R
T
S
T
O
P
IDENTIFICATION
BYTE
FIRST DATA
BYTE
A
C
K
SIGNALS FROM
THE MASTER
SIGNALS FROM
THE ISL12057
A
C
K
10
0
11
A
C
K
WRITE
SIGNAL AT SDA
00 00
000
ADDRESS
BYTE
A
C
K
LAST DATA
BYTE
A
C
K
FIGURE 10. SLAVE ADDRESS, WORD ADDRESS, AND DATA
BYTES
SLAVE
ADDRESS BYTE
D7
D6
D5
D2
D4
D3
D1
D0
A0
A7
A2
A4
A3
A1
DATA BYTE
A6
A5
1
10
0
1
0
R/W
0
WORD ADDRESS
ISL12057
发布紧急采购,3分钟左右您将得到回复。
相关PDF资料
ISL12058IUZ
IC RTC/CALENDAR I2C-BUS 8-MSOP
ISL12059IBZ
IC RTC/CALENDAR I2C-BUS 8-SOIC
ISL12082IUZ
IC RTC I2C LO-POWER 10-MSOP
ISL1208IU8-TK
IC RTC/CALENDAR I2C 8-MSOP
ISL1209IU10-TK
IC RTC/CALENDAR I2C 10-MSOP
ISL1218IUZ
IC RTC LP BATT BACKED SRAM 8MSOP
ISL1219IUZ-T
IC RTC LP BATT BACK SRAM 10MSOP
ISL1220IUZ
IC RTC LP BATT BACK SRAM 10MSOP
相关代理商/技术参数
ISL12057IUZ-T
功能描述:实时时钟 REAL TIME CLK W/ ALARM DS1337 COMP RoHS:否 制造商:Microchip Technology 功能:Clock, Calendar. Alarm RTC 总线接口:I2C 日期格式:DW:DM:M:Y 时间格式:HH:MM:SS RTC 存储容量:64 B 电源电压-最大:5.5 V 电源电压-最小:1.8 V 最大工作温度:+ 85 C 最小工作温度: 安装风格:Through Hole 封装 / 箱体:PDIP-8 封装:Tube
ISL12058
制造商:INTERSIL 制造商全称:Intersil Corporation 功能描述:Low Cost and Low Power I2C-Bus? Real Time Clock/Calendar
ISL12058IBZ
功能描述:实时时钟 REAL TIME CLK W/ ALARM & TIMR FUNCTNS RoHS:否 制造商:Microchip Technology 功能:Clock, Calendar. Alarm RTC 总线接口:I2C 日期格式:DW:DM:M:Y 时间格式:HH:MM:SS RTC 存储容量:64 B 电源电压-最大:5.5 V 电源电压-最小:1.8 V 最大工作温度:+ 85 C 最小工作温度: 安装风格:Through Hole 封装 / 箱体:PDIP-8 封装:Tube
ISL12058IBZ-T
功能描述:实时时钟 REAL TIME CLK W/ ALARM & TIMR FUNCTNS RoHS:否 制造商:Microchip Technology 功能:Clock, Calendar. Alarm RTC 总线接口:I2C 日期格式:DW:DM:M:Y 时间格式:HH:MM:SS RTC 存储容量:64 B 电源电压-最大:5.5 V 电源电压-最小:1.8 V 最大工作温度:+ 85 C 最小工作温度: 安装风格:Through Hole 封装 / 箱体:PDIP-8 封装:Tube
ISL12058IRTZ
功能描述:实时时钟 REAL TIME CLK W/ ALARM & TIMR FUNCTNS RoHS:否 制造商:Microchip Technology 功能:Clock, Calendar. Alarm RTC 总线接口:I2C 日期格式:DW:DM:M:Y 时间格式:HH:MM:SS RTC 存储容量:64 B 电源电压-最大:5.5 V 电源电压-最小:1.8 V 最大工作温度:+ 85 C 最小工作温度: 安装风格:Through Hole 封装 / 箱体:PDIP-8 封装:Tube
ISL12058IRTZ-T
功能描述:实时时钟 REAL TIME CLK W/ ALARM & TIMR FUNCTNS RoHS:否 制造商:Microchip Technology 功能:Clock, Calendar. Alarm RTC 总线接口:I2C 日期格式:DW:DM:M:Y 时间格式:HH:MM:SS RTC 存储容量:64 B 电源电压-最大:5.5 V 电源电压-最小:1.8 V 最大工作温度:+ 85 C 最小工作温度: 安装风格:Through Hole 封装 / 箱体:PDIP-8 封装:Tube
ISL12058IRUZ-T
功能描述:实时时钟 REAL TIME CLK W/ ALARM & TIMR FUNCTNS RoHS:否 制造商:Microchip Technology 功能:Clock, Calendar. Alarm RTC 总线接口:I2C 日期格式:DW:DM:M:Y 时间格式:HH:MM:SS RTC 存储容量:64 B 电源电压-最大:5.5 V 电源电压-最小:1.8 V 最大工作温度:+ 85 C 最小工作温度: 安装风格:Through Hole 封装 / 箱体:PDIP-8 封装:Tube
ISL12058IUZ
功能描述:实时时钟 REAL TIME CLK W/ ALARM & TIMR FUNCTNS RoHS:否 制造商:Microchip Technology 功能:Clock, Calendar. Alarm RTC 总线接口:I2C 日期格式:DW:DM:M:Y 时间格式:HH:MM:SS RTC 存储容量:64 B 电源电压-最大:5.5 V 电源电压-最小:1.8 V 最大工作温度:+ 85 C 最小工作温度: 安装风格:Through Hole 封装 / 箱体:PDIP-8 封装:Tube